Combining ultrasensitive motion detectors with thermal sound-emitting technology, scientists in China have come up with an “artificial throat” that could enable speech in people with damaged or nonfunctioning vocal cords.
The American Chemical Society has posted the study’s abstract, along with video demonstrations, in its journal ACS Nano.
Team members, most of whom work at Tsinghua University in Beijing, fabricated a homemade circuit board on which to build out their dual-mode system combining detection and emitting technologies, according to the authors.
During the device’s development phase, the system transformed subtle throat movements into simple sounds like “OK” and “No.”
The sound and motion detection/emission system can “enable graphene to achieve device-level applications to system-level applications, and those graphene acoustic systems are wearable [due to their] miniaturization and light weight,” the authors explain.
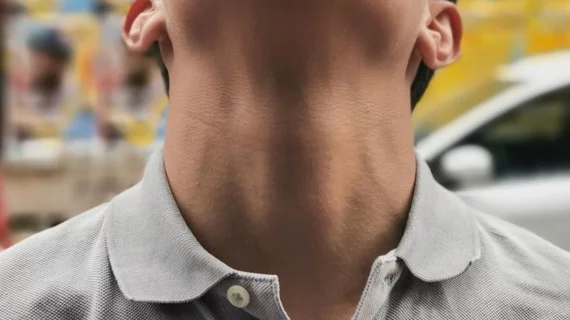
In a news release, the ACS describes the skinlike device—called the WAGT, for wearable artificial graphene throat (WAGT)—as similar to a temporary tattoo, at least as perceived by the wearer.
To make the device functional and flexible, the scientists laser-scribed graphene on a thin sheet of polyvinyl alcohol film, ACT explains.
The appliance is about the size of two thumbnails side by side.
“The researchers used water to attach the film to the skin over a volunteer’s throat and connected it with electrodes to a small armband that contained a circuit board, microcomputer, power amplifier and decoder,” ACT reports.
In trials of the device, a volunteer noiselessly imitated the throat motions of speech during a trial of the device—and the instrument converted these movements into single-syllable words.
In the future, according to ACT, “mute people could be trained to generate signals with their throats that the device would translate into speech.”